Liposomes: Power of Intravenous Therapy in Oral Delivery
The word liposome is derived from Greek terms “lipos” – fat, and “soma” body. There is a lot of science behind this, but we would like to translate it into a more digestible, less intimidating language. Simply put, it is a ball of fat with two layers of phospholipids, one layer being hydrophilic (attracting water) and the other being lipophilic (attracting fats). Every cell’s membrane is also made of a similar two-layer structure.
Imagine a liposome as a fat-based three-dimensional ball-shaped cage that is able to contain, protect, and carry a particular molecule from one place in the body to another. For example, Vitamin C, which is a water-soluble vitamin, “trapped” in this fatty liposomal cage can be easily taken to the area of the body where it belongs, instead of just passing through the digestive system, not being absorbed and being eliminated with urine.
We recognize three different types of liposomes based on their size and structure, which determines not only how much of the nutrient is encapsulated inside of it, but also the half-life of the molecule (how long does it take before the lipid layer gets broken down and the nutrient is released and absorbed in the body).
Why are Liposomes Better?
Liquid liposomal supplements are a great alternative for those who have problems swallowing pills, and one of their greatest benefits is the ability to transport nutrients right where they belong, which is our cells. They can carry water-soluble and fat-soluble nutrients effectively, and protect them on the way to our cells, so the amount of nutrients lost during the transport is minimal, compared to non-liposomal pills and powders.
Even though they can cost more initially, you are actually going to get more bang for your buck! For example, common Vitamin C supplements have a rate of absorption around 8%, the rest of what you ingest gets eliminated with urine. Liposomal Vitamin C has a rate of absorption up to 95%! See the difference? I personally want to get maximum out of the supplements I pay for, I don’t want to pee out most of it and experience little to no benefits! That would be a really expensive pee!
What Liposomal Nutrients are Available?
There are a few different nutrients available in this form on the market, and there are also many different brands that make liposomes. They are not all made the same, so choosing the right brand is also important. Lipids are quite fragile, sensitive to light and temperature, so how and where things are made should matter to you as a consumer.
Our trusted brands we stand by are Purality Health and QuickSilver Scientific. They offer several key nutrients in the liposomal form known to be vitally important for the optimal function of a human body.
Liposomal Delivery Boosts Bioavailability up to 1500%
This high tech delivery system – Liposomal Delivery (LD) – for nutritional supplements uses proven nanochemistry to increase their effectiveness 10 to 15 times.
The History of Liposomes
Liposomes were discovered by Alec D. Bangham in 1961 (Journal of Molecular Biology 8:660-8 (1964), and Liposomal Delivery (LD) started developing in the 1970s.
For its first 25 years or so, LD was used almost exclusively by medical researchers to deliver drugs, dyes or other therapeutic agents to specific tissues. From then until now, only a few companies have used LD in non-medical applications, like we see in Liposomal Turmeric.
Because of its superior ability to transport substances through the skin, some companies use LD for topical moisturizers, cell therapy and anti-aging cosmetic products. A smaller number of companies now use LD for oral delivery of supplements. With the impressive benefits of LD, you can expect more companies to start using it soon.
Liposomal Delivery Is Powerful
LD encapsulation protects supplements from most of the degrading and inhibitory factors of the digestive system, with unparalleled payload protection.
Some liposomes release their contents at a certain temperature, others at a specific pH, while others do so in the presence of other substances. They function like microscopic smart delivery vehicles that can travel through the body and release their payload at the desired location.
LD is so powerful that it delivers more substances to targeted tissues and organs than any other method. It is so efficient that dose levels can be 10 to 15 times smaller. Reductions of this magnitude have tremendous therapeutic and economic implications.
Factors that Affect Bioavailability
The bioavailability of supplements can be drastically reduced before they are absorbed by many factors:
- Moisture, oxygen and other factors in the environment
- Enzymes and digestive juices in the mouth and stomach
- Bile salts in the intestines
- Friendly and unfriendly organisms in the intestines
- Food and drug interactions in the digestive system
- Additives, coatings, binders, fillers, sugars, colors and flavors added to enhance packaging or facilitate swallowing
- Incomplete assimilation due to partial or non-breakdown of tablet or capsule into small enough particles for uptake in the intestines.
Liposomal Delivery Uses Essential Phospholipids
Liposomal Turmeric uses Essential Phospholipid liposomes to form a barrier around their contents that is resistant to digestive juices, alkaline solutions, salts and free radicals. Phospholipids do a superior job of protecting the encapsulated contents from oxidation and degradation. Most importantly, this protective barrier stays intact until the contents have been delivered to the system, organ, gland or cell where the contents will be used.
Essential phospholipids that are used to make liposomes have their own health benefits.
Phospholipids are essential for the formation all cell membranes – the skin for every cell – to keep the insides in and the outsides out. Phospholipid membranes protect cells from attack from toxins, pathogens and free radicals that can inhibit or stop the necessary functions of every cell.
When you ingest phospholipids, your body uses them to replace damaged material, making every cell membrane healthier – more able to protect and nourish the cells they encase.
The importance of phospholipids is so great that encapsulation to deliver a nutrient may provide even more health benefits than the substances inside.
Finally, in contrast to some tablets, pills and capsules that can be eliminated in the stool partially digested or totally intact, the sub-microscopic size and structure of liposomes recognized by the body as a friendly substance, allowing them to be moved through digestive, lymphatic and circulatory systems with ease.
The Phospholipid Miracle That Makes LD Possible
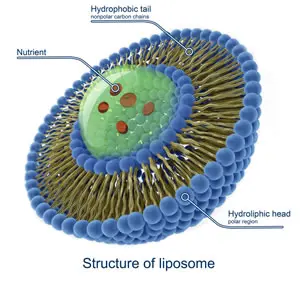
Each phospholipid molecule has three major parts, one head and two tails. The head is made from three molecular components: choline, phosphate, and glycerol. The head is hydrophilic (attracted to water), the tail is a long fatty acid chain that is hydrophobic (repelled by water).
When phospholipids are added to water-based solution, the hydrophilic heads of the lipids form a line side by side with their tails behind much like swimmers at a starting gate. Because the tails are hydrophobic, another phospholipid layer will line itself up tail-to-tail in response to the environment. This natural alignment creates two rows of tightly packed phospholipid molecules, called a phospholipid bilayer. It is these phospholipid bilayers that form the membranes around and within every cell in our bodies. One thousand of these bilayers are the thickness of paper.
Phospholipid bilayers form the cell membrane by arranging themselves with the heads of the phospholipids making up the external and internal surfaces of the cell. This holds the contents of the cell in and protects them from harmful substances on the outside.
A combination of different proteins interspersed within the phospholipid bilayers in every cell provides channels for nutrients and cellular waste products to pass through.
There are several types of phospholipids. Some can be synthesized in your liver, but some have to be ingested. Phosphatidylcholine that we use to make the liposomes is such required essential polyunsaturated fatty acid. Linoleic acid and gamma-linolenic acid are essential because they cannot be synthesized in the human body; they must be supplied by the food we eat. Phosphatidyl Cholines (PCs) are a subset of essential phospholipids.
The physical properties of fats, oils, and fatty acids can change substantially as the chains become more unsaturated (drop hydrogen from the chain). Lard, butter and bacon are examples of saturated fats, solid at room temperature and more viscous. Polyunsaturated fats are more runny and thin, and polyunsaturated PC quickly replaces the more saturated and/or damaged phospholipids in plasma membranes, essentially clearing low-density lipids and cholesterol, making blood and lymph healthier. Plasma membranes return to a more efficient, more fluid state, and hardened saturated fats and cholesterol that have become lodged there are removed and metabolized. Cells throughout the body become more able to resist the damaging effects of free radical attack.
The Structure of Liposomes
PC liposomes are the spheres that encapsulate the supplement (payload) to be delivered.
The size of a liposome is determined by the process used to make them. Diameters can range from 0.1 to hundreds of micrometers. The BI-layer liposomes provide the best combination of protection and efficiency. Smaller liposomes are better at protecting and delivering the payload than larger ones.
Phosphatidylcholine can be extracted from lecithin, or synthesized in a laboratory. For food supplements, PC from sunflower lecithin seems to be the best liposomal lipid.
Having a liposomal size under 200 nanometers will provide increased stability and protection.
Health and Anti-Aging Benefits of Essential Phospholipids
- Reduction in total serum lipids (fat in the blood)
- Reduction in LDL (bad) cholesterol
- Increase in HDL (good) cholesterol
- Lowers serum triglycerides and overall cholesterol
- Reduction in triglycerides
- Reduction in cholesterol deposits in vascular walls
- Reduction in blood platelet aggregation (detrimental tendency of blood cells to stick together)
- Effective antioxidant in lipids
- Increase in red blood cell fluidity
- Reduced viscosity
- Improved coronary circulation
- Increased exercise tolerance
- Improved peripheral circulation (hand and feet)
- Liver protection and rejuvenation
- Improved immunity
- Improved memory
- Prevention of excess collagen formation and cross-linking (wrinkles and scarring).
![[PTVB] Active B Complex](/web/image/product.template/2187/image_1920/%5BPTVB%5D%20Active%20B%20Complex?unique=ae82545)
![[PTVB12] B12 with Fulvic Acid](/web/image/product.template/3034/image_1920/%5BPTVB12%5D%20B12%20with%20Fulvic%20Acid?unique=ae82545)
![[QS-1042] Bitter X](/web/image/product.template/3044/image_1920/%5BQS-1042%5D%20Bitter%20X?unique=ae82545)
![[QS-1014] Bitters No. 9](/web/image/product.template/3045/image_1920/%5BQS-1014%5D%20Bitters%20No.%209?unique=ae82545)
![[QS-1087] Cat's Claw Elite](/web/image/product.template/3069/image_1920/%5BQS-1087%5D%20Cat%27s%20Claw%20Elite?unique=ae82545)
![[QS-1026] CoQ10](/web/image/product.template/3089/image_1920/%5BQS-1026%5D%20CoQ10?unique=ae82545)
![[QS-1229] Crypto Co-Max](/web/image/product.template/3102/image_1920/%5BQS-1229%5D%20Crypto%20Co-Max?unique=ae82545)
![[QS-1230] Cryptolepis](/web/image/product.template/3103/image_1920/%5BQS-1230%5D%20Cryptolepis?unique=ae82545)
![[QS-1004] EDTA with R-Lipoic Acid](/web/image/product.template/3134/image_1920/%5BQS-1004%5D%20EDTA%20with%20R-Lipoic%20Acid?unique=ae82545)
![[QS-1241] Ergo-Thione+](/web/image/product.template/34651/image_1920/%5BQS-1241%5D%20Ergo-Thione%2B?unique=f4a30d3)
![[QSGT] Glutathione](/web/image/product.template/3195/image_1920/%5BQSGT%5D%20Glutathione?unique=ae82545)
![[QS-1057] Melatonin](/web/image/product.template/3284/image_1920/%5BQS-1057%5D%20Melatonin?unique=ae82545)
![[QS-1008] Methyl B-12](/web/image/product.template/3288/image_1920/%5BQS-1008%5D%20Methyl%20B-12?unique=ae82545)
![[QS-1127] NAD+ Gold](/web/image/product.template/3310/image_1920/%5BQS-1127%5D%20NAD%2B%20Gold?unique=ae82545)
![[QS-1999] NanoFuel](/web/image/product.template/3312/image_1920/%5BQS-1999%5D%20NanoFuel?unique=ae82545)
![[RLRM] Receptimet](/web/image/product.template/3397/image_1920/%5BRLRM%5D%20Receptimet?unique=ae82545)
![[QS-1025] The ONE](/web/image/product.template/3462/image_1920/%5BQS-1025%5D%20The%20ONE?unique=420f881)
![[PTTU] Turmeric](/web/image/product.template/3481/image_1920/%5BPTTU%5D%20Turmeric?unique=ae82545)
![[QS-1033] Vitamin C](/web/image/product.template/3495/image_1920/%5BQS-1033%5D%20Vitamin%20C?unique=65304cd)
![[QS-1003] Vitamin C with R-Lipoic Acid](/web/image/product.template/34593/image_1920/%5BQS-1003%5D%20Vitamin%20C%20with%20R-Lipoic%20Acid?unique=0c05cf0)
![[PTDK] Vitamin D3](/web/image/product.template/3497/image_1920/%5BPTDK%5D%20Vitamin%20D3?unique=ae82545)